
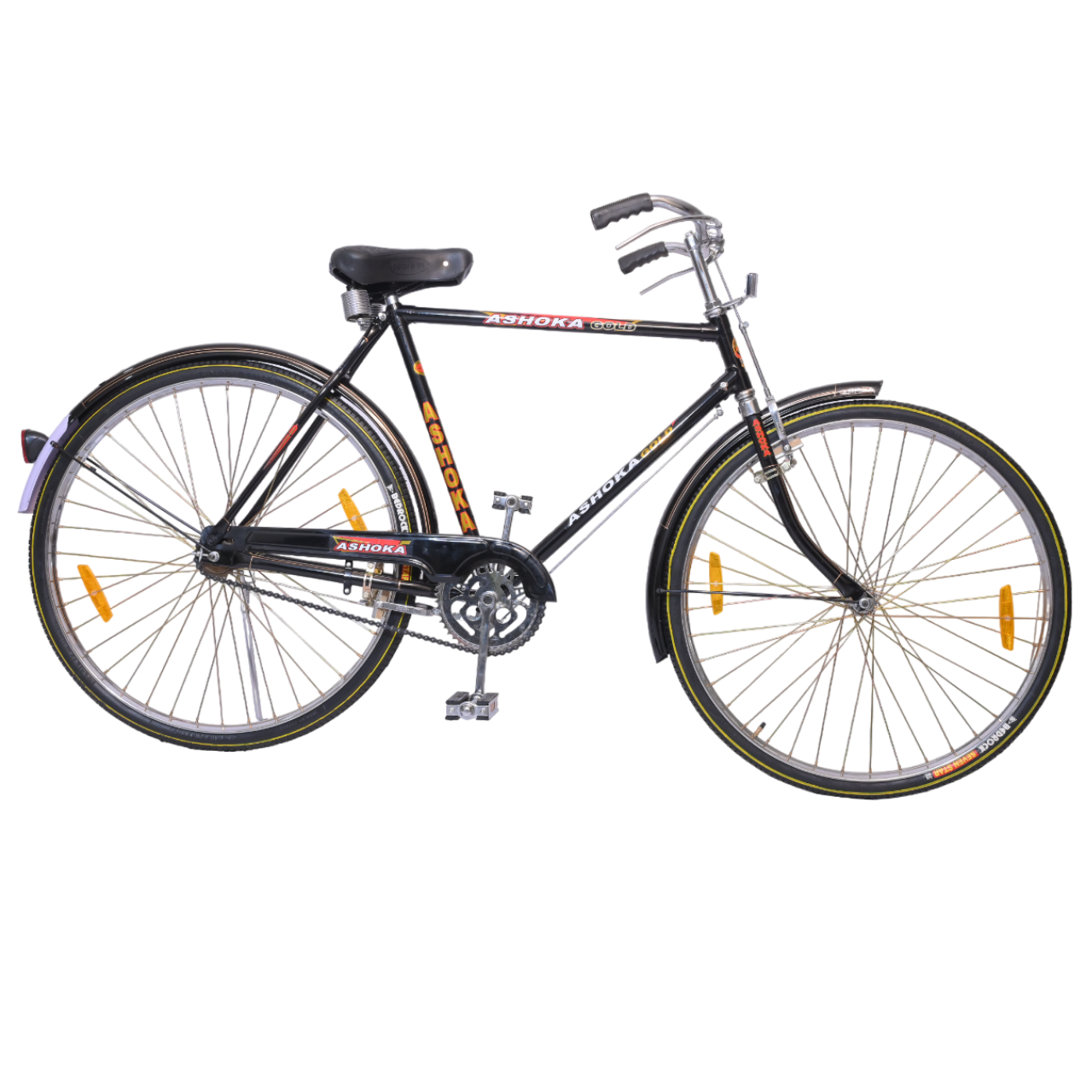
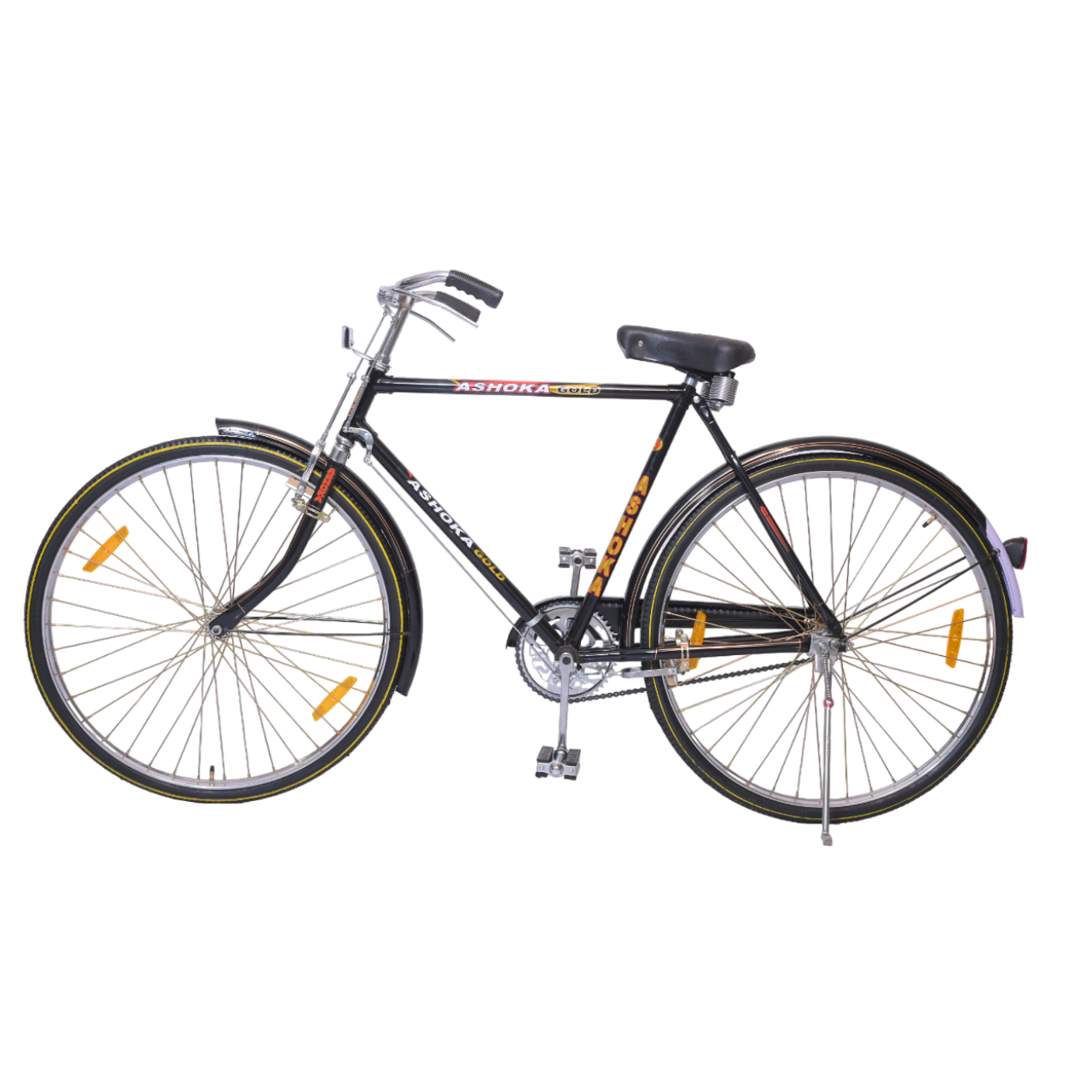
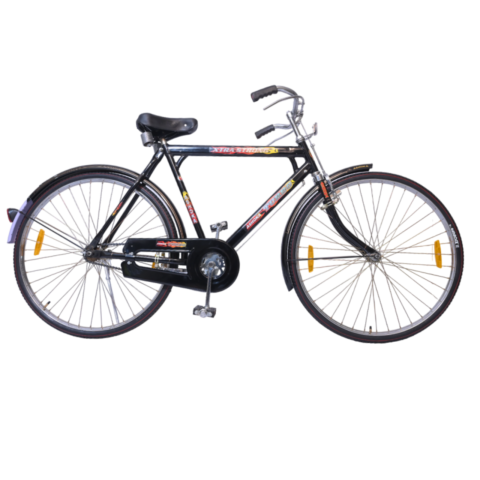
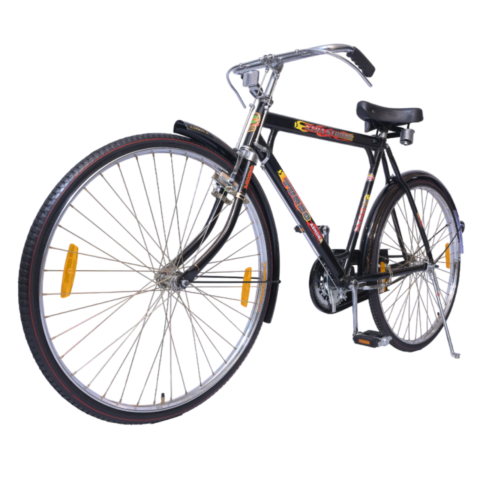
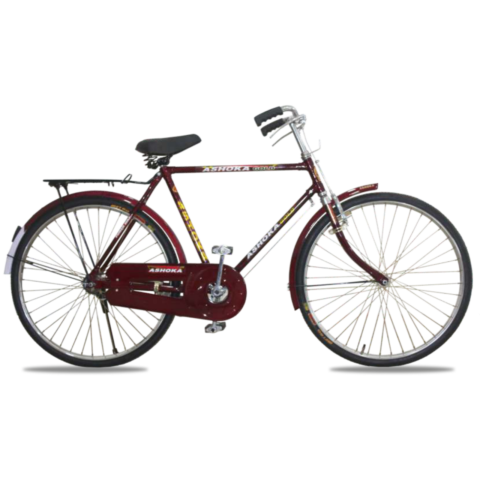
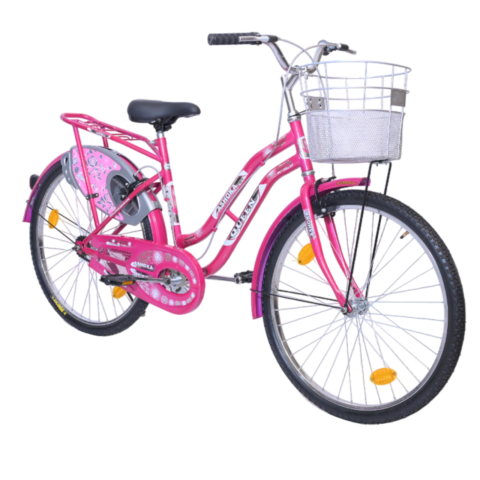
Ashoka Gold PH/T 22 inch
Rated 5.00 out of 5 based on 1 customer rating
1 customer review
₹5,649.00
Add to cartAshoka Gold PH/T 22 inch
Rated 5.00 out of 5 based on 1 customer rating
1 customer review
₹5,649.00
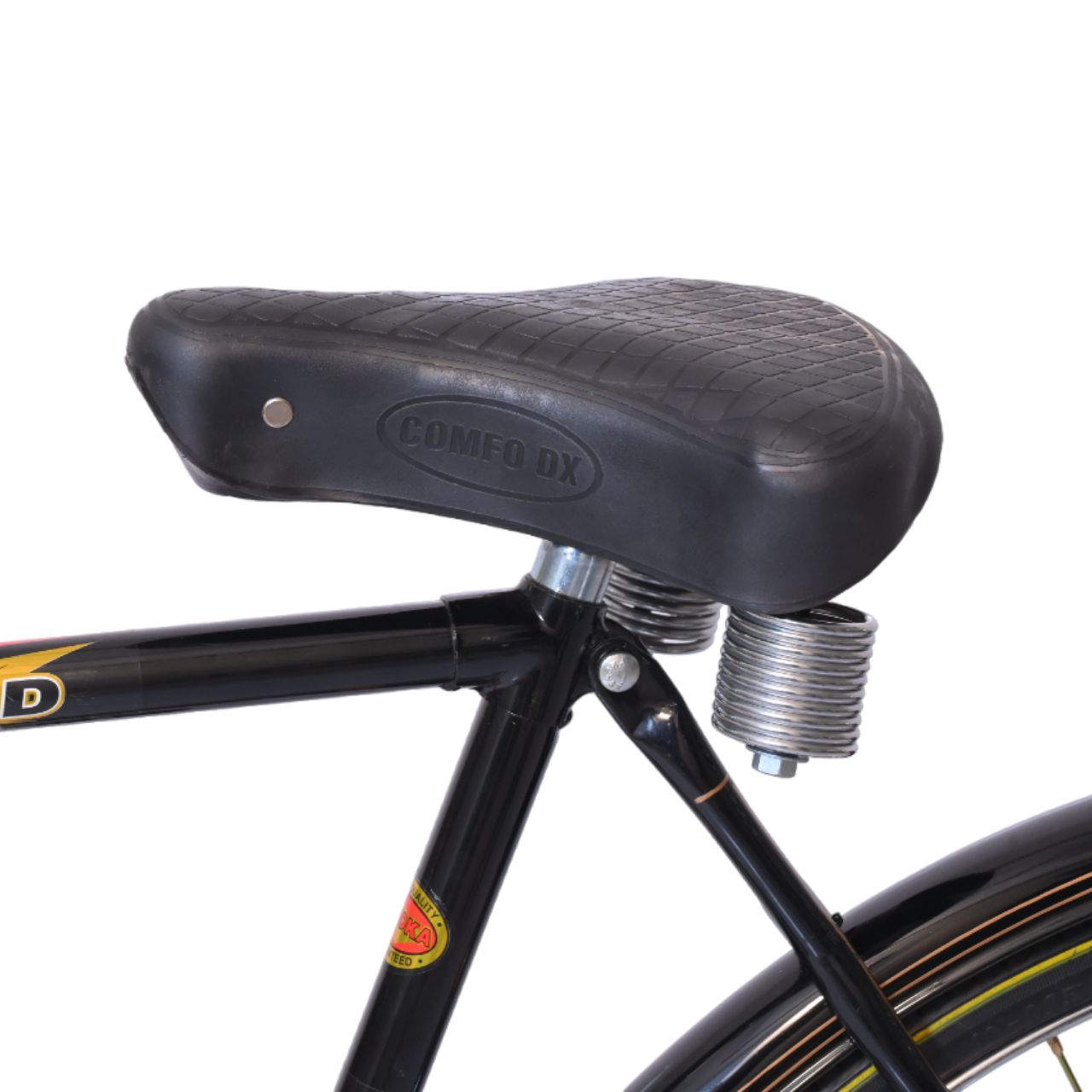
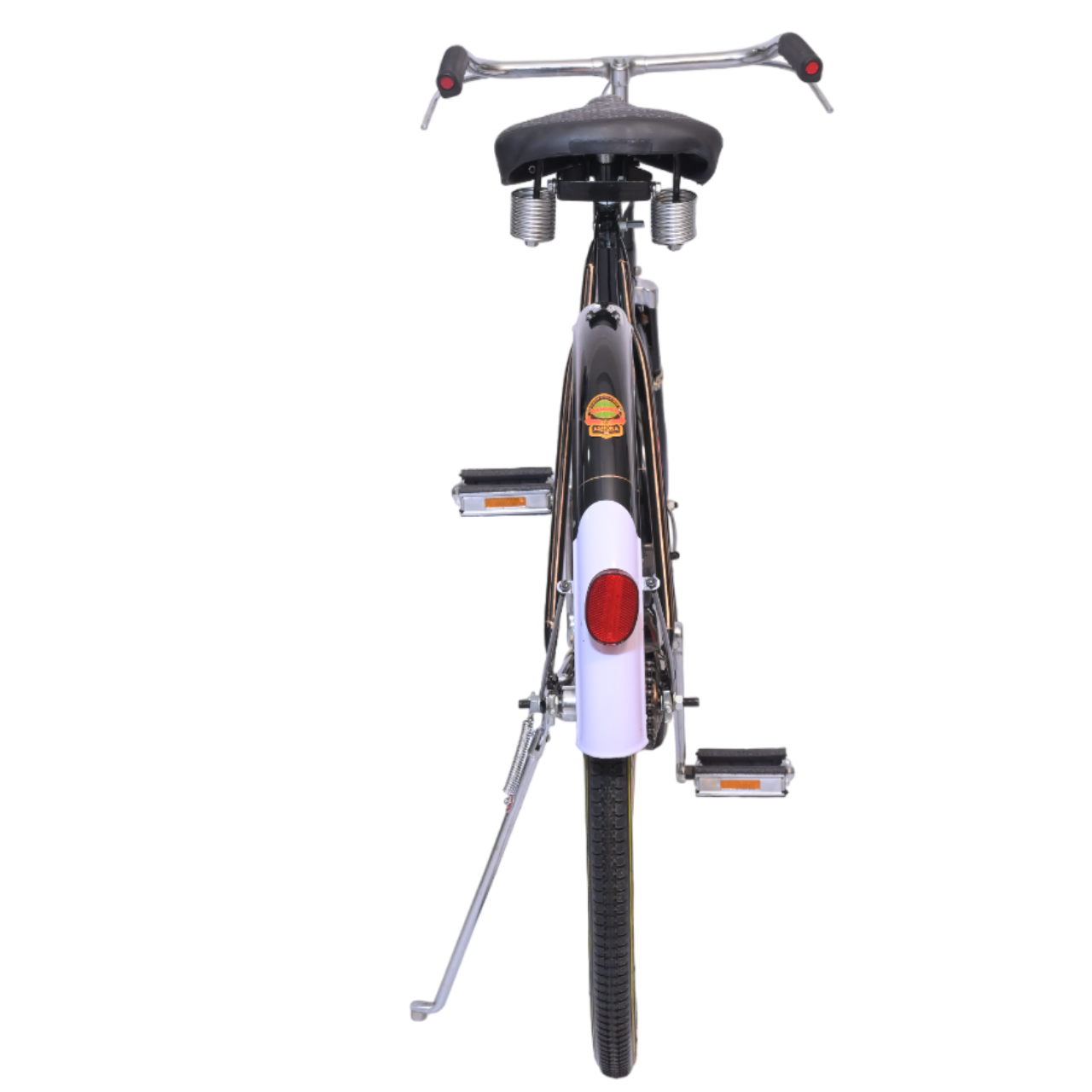
COLOUR BLACK (FRAME HEAVY,H/D PEDAL S/BODY SEAT COMFO DX,CLASIC CHAIN COVER,40X40H.HUB RIM 40H.,SPOK 12G. C/W 48T & NYLON TYRE)
(28x11h)
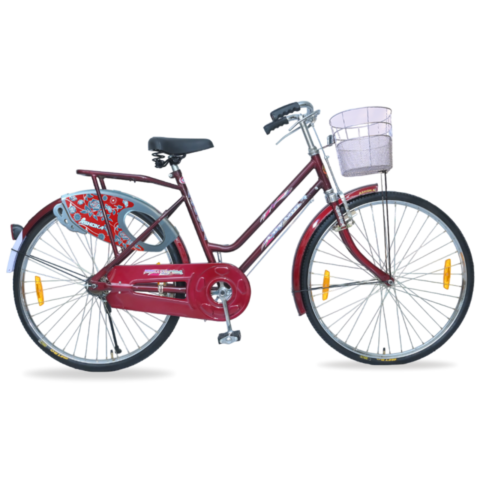
Available Colors
Black
Lazer Red
Green
| Component | Specification |
|---|---|
| Frame | 220/24″ C.R. Pipe Frame |
| Brake | Steel Brake |
| Fork | 22/24″ |
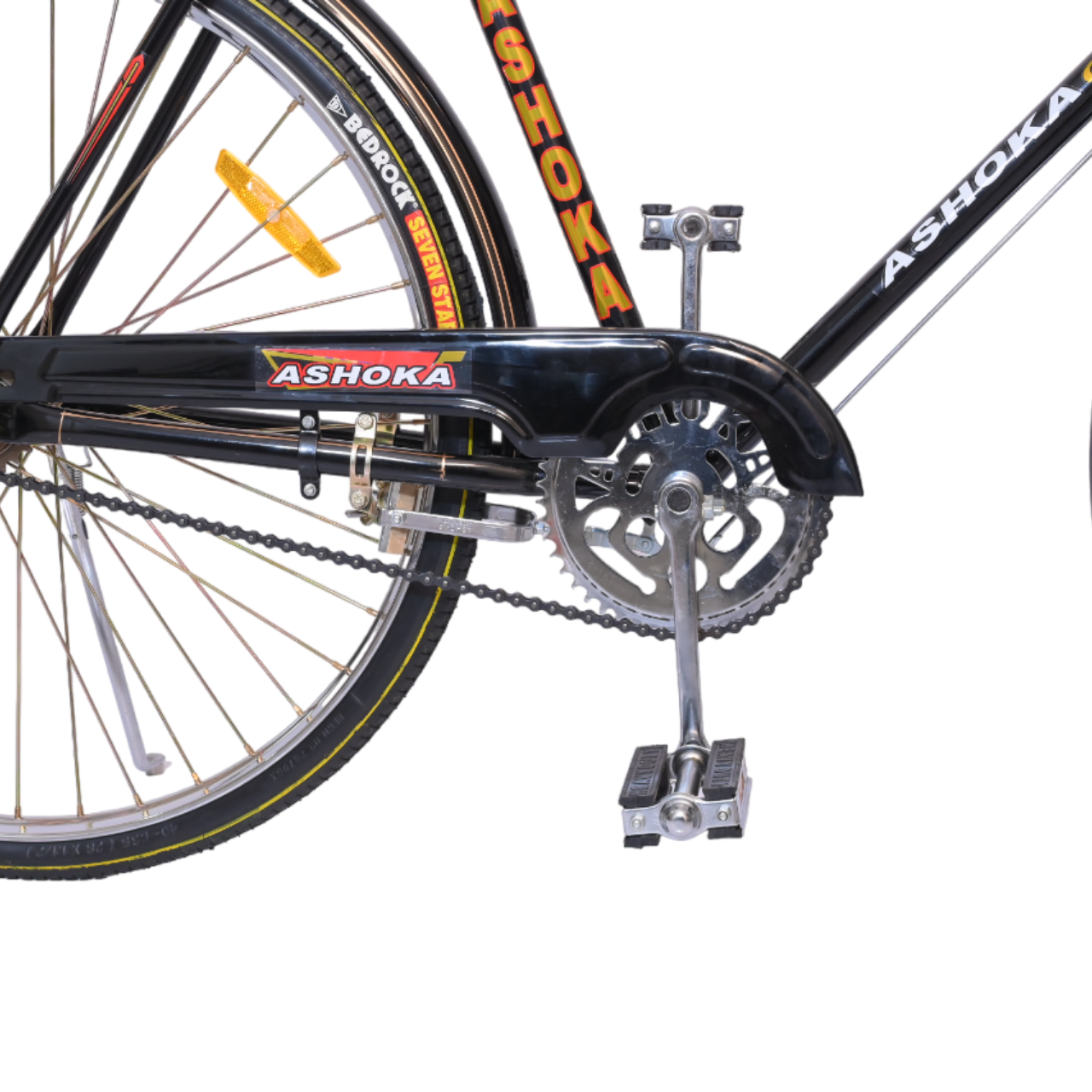
| Chainring | 48T BCP |
| Tyre/Tube | 28 x 1.5 |
| Rim | High Quality 28 x 1.5 |
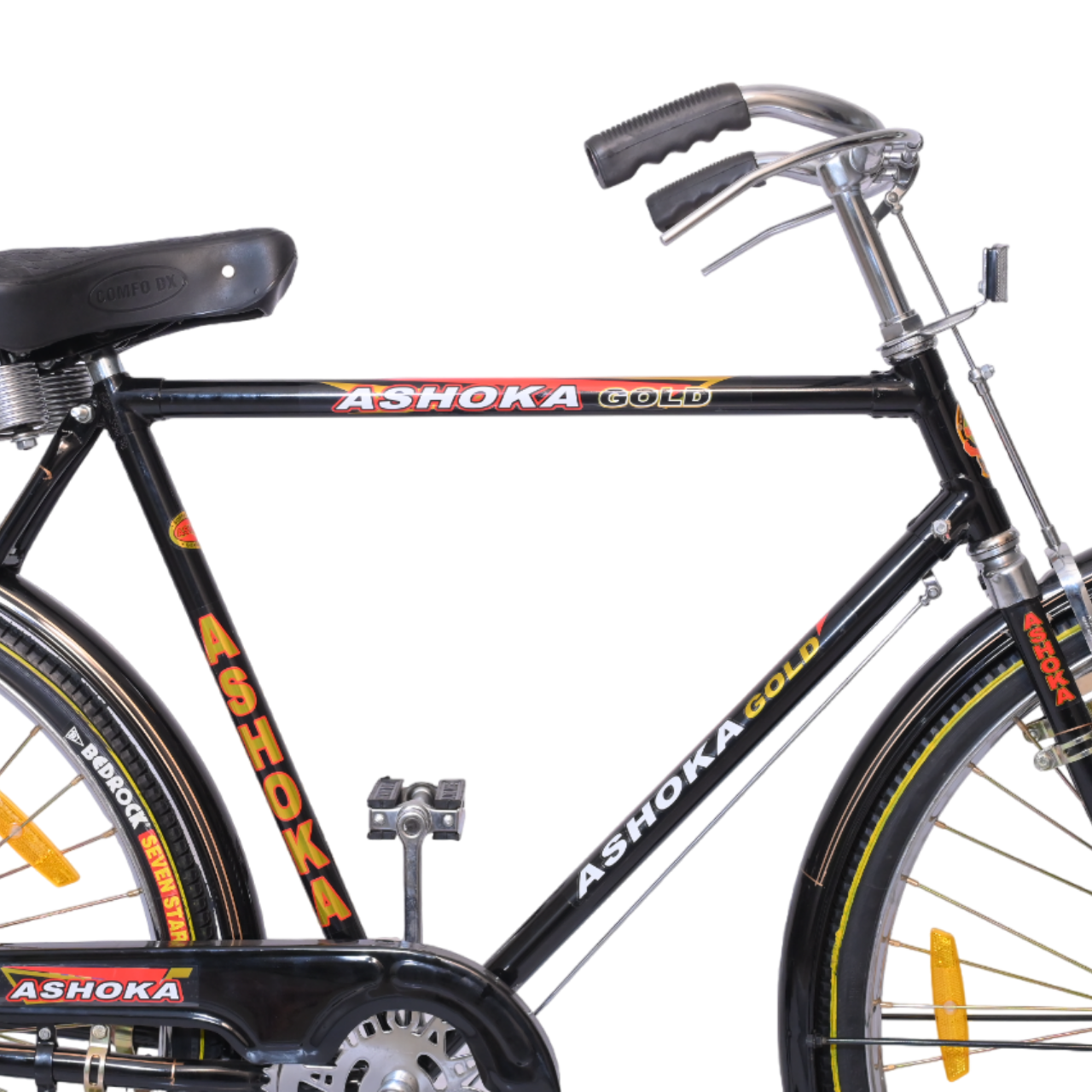
| Saddle | Comfo Dx |
| Spokes | 12 Gauge |
| Chain Cover | Classic |
| Pedal | Heavy Steel Pedal |
| Hub | 40 x 40 |
Add to cart
Buy Now
Main Components of a Bicycle
A bicycle is a two-wheeled vehicle powered by human effort, designed for transportation, exercise, or recreation. It is a highly efficient and environmentally friendly mode of transport. Below is a detailed description of its main components and features:
Frame:
- The structural backbone of the bicycle, usually made from materials like steel, aluminum, carbon fiber, or titanium.
- It connects all other parts and comes in various shapes and sizes to suit different riding styles (e.g., road, mountain, hybrid).
Wheels:
- Comprised of a rim, spokes, and a hub, the wheels provide balance and movement.
- Fitted with tires, which may vary in size and tread depending on terrain (e.g., smooth tires for roads, knobby tires for trails).
Handlebars:
- Used for steering and controlling the bicycle.
- Styles include flat handlebars (common in mountain bikes) and drop handlebars (found on road bikes).
Saddle (Seat):
- The part where the rider sits, designed for comfort and support.
- Often adjustable to suit the rider’s height.
Pedals:
- Located on the crank arms, pedals are where the rider places their feet to propel the bike forward.
Chain and Drivetrain:
- The chain connects the pedals to the rear wheel, transferring energy from the rider to the bike.
- Includes gears and derailleurs for adjusting resistance and speed.
Brakes:
- Essential for stopping and controlling speed. Types include rim brakes, disc brakes, and coaster brakes.
Gears (Optional):
- Bicycles may have multiple gears to help with pedaling in different conditions (e.g., hills, flat roads).
Fork:
- The part of the frame that holds the front wheel and connects it to the handlebars.
- May include suspension in mountain bikes to absorb shocks.
Kickstand (Optional):
- A small stand used to keep the bicycle upright when parked.
Accessories (Optional):
- Lights and reflectors: For visibility, especially at night.
- Bell or horn: For signaling.
- Basket or rack: For carrying items.
Types of Bicycles
- Road Bikes: Lightweight and designed for speed on paved roads.
- Mountain Bikes: Built for off-road trails with features like suspension and wide tires.
- Hybrid Bikes: A mix of road and mountain bike features, suitable for diverse terrain.
- Electric Bikes (E-bikes): Equipped with a motor for assisted pedaling.
- Cruiser Bikes: Stylish, comfortable bikes for casual riding.
- Folding Bikes: Compact and portable, ideal for commuting.
Key Features and Benefits
- Human-Powered: Propelled by pedaling, making it energy-efficient and eco-friendly.
- Simple Mechanics: Easy to maintain and repair.
- Affordable: Cost-effective transportation compared to motor vehicles.
- Health Benefits: Promotes cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength, and mental well-being.
Bicycles are a timeless invention, cherished for their versatility and positive impact on health and the environment. Whether for fun, fitness, or function, bicycles continue to be a popular and practical choice worldwide. 🚴♀️
1 review for Ashoka Gold PH/T 22 inch
Add a review Cancel reply
User Guide
Please read the manual before use.
1. Preparation Before Riding
Choose the Right Bike
- Ensure the bicycle fits your height. You should be able to touch the ground with your toes while sitting on the saddle.
Check Your Equipment
- Tires: Make sure they are properly inflated.
- Brakes: Squeeze the brake levers to confirm they work.
- Chain: Ensure the chain is clean and well-lubricated.
- Lights/Reflectors: If riding at night, make sure the bike has functioning lights and reflectors.
Wear Safety Gear
- Helmet: Properly fit the helmet to protect your head.
- Gloves, elbow pads, and knee pads (optional).
Dress Appropriately
- Avoid loose clothing that might get caught in the chain or wheels.
- Wear bright or reflective clothing for visibility.
2. Mounting the Bicycle
- Stand on one side of the bike.
- Hold the handlebars with both hands for balance.
- Swing one leg over the frame and position yourself on the saddle.
- Place one foot on the ground and the other on a pedal in its lowest position.
3. Starting to Ride
- Push off with the foot on the ground to get momentum.
- Simultaneously press down on the pedal with your other foot.
- Place both feet on the pedals and start pedaling evenly.
4. Steering and Balancing
- Steering: Use the handlebars to guide the bicycle in the desired direction. Keep your movements smooth and controlled.
- Balancing: Look ahead, not down. Balance improves with speed, so don’t go too slowly.
5. Braking
- Gently squeeze the brake levers on the handlebars.
- Use both brakes (front and rear) for smooth stopping.
- Avoid using only the front brake as it can cause the bike to flip forward.
6. Turning
- Slow down before turning.
- Lean slightly into the turn while steering in the same direction.
- Keep your inside pedal raised to avoid hitting the ground.
7. Gears (If Applicable)
- Use low gears for uphill or starting off.
- Use higher gears for flat or downhill riding.
- Shift gears gently while pedaling.
8. Safety Tips
- Always ride on the correct side of the road (usually the right-hand side).
- Follow traffic rules, signals, and signs.
- Signal turns using hand signals:
- Left turn: Extend your left arm straight out.
- Right turn: Extend your left arm bent upward or your right arm straight out.
- Stay alert for pedestrians, cars, and obstacles.
- Avoid distractions like using your phone while riding.
9. Parking the Bicycle
- Slow down and come to a stop using your brakes.
- Dismount the bike by stepping off to one side.
- Park your bike in a designated rack or secure it with a lock.
With practice, you’ll gain confidence and enjoy the freedom of cycling. Happy riding! 🚴♂️































admin –
I have been a Themeforest customer since November 2017. This Author has the best support they have ever given me